Employee Wi-Fi Security Guide: Strategies and Rule Development
Analyze hidden corporate Wi-Fi risks using AI and follow our step-by-step guide to establishing security rules. This guide helps businesses minimize threats like data leaks and unauthorized access, ensuring a safe and reliable network environment for all employees.

Tools Used
Sensei AI - Optimized for the hospitality industry and more.
Why Wi-Fi Security Measures are Essential
Are work and personal devices connected to the same network? Is the same password shared among all employees and left unchanged for long periods? The Wi-Fi networks employees use daily often harbor serious security risks, such as data leaks, unauthorized access, and malware infections.
Establishing an environment where employees can use Wi-Fi safely is crucial for protecting information assets and maintaining corporate trust.
Using examples from the hospitality industry, this guide explains the specific steps for creating Wi-Fi rules applicable to any business implementing employee-only Wi-Fi.
Specific Steps
Step 1: Assessing the Current Situation and Identifying Potential Risks
To minimize the risk of data leaks, it is vital to accurately understand the potential vulnerabilities in your current environment and clarify existing challenges.
1-1. Inventory of Devices and Wi-Fi Usage
First, organize your current Wi-Fi usage as follows:
[Types of Devices Used by Employees]
- Business Laptops
- Usage: Accessing internal systems and customer information.
- Personal Smartphones
- Usage: Business communication, information searching, and using some work apps.
- Tablets
- Usage: Accessing specific work apps and viewing training materials.
[Current Wi-Fi Usage Status]
- Network Configuration
- Status: Only one SSID is used, with no distinction between work and personal use.
- Access Permissions
- Status: Internet access from personal smartphones is permitted, in addition to internal system access.
- Password Settings
- Status: Passwords are changed periodically, but the level of complexity is standard.
- Security Education
- Status: Employee security training is limited to minimal reminders.
1-2. Risk Analysis via AI
Provide the information gathered above to Sensei AI with the following instructions to request a risk analysis. Including specific examples in the output will help improve understanding.
[Types of Devices]
Business Laptops (used for internal systems)
Personal Smartphones (used for communication, searching, and some apps)
Tablets (used for apps and training materials)
[Current Wi-Fi Status]
Both internal systems and personal internet use are allowed on the same network.
There is only one SSID for both work and personal use.
Passwords are changed regularly but are not highly complex.
Security education is minimal."

The AI will identify potential risks (e.g., malware infection from personal devices, unauthorized access, or data leaks) based on the provided data.
This output can also serve as a resource to deepen internal understanding of current risks. In the next step, we will create shared company rules based on this analysis.
Step 2: Developing Practical and Easy-to-Understand Rules
Based on the risks identified in Step 1, establish "Usage Rules" and "Security Settings" as countermeasures. Instruct the AI to create rules using clear, specific language so that all employees, regardless of their technical knowledge, can easily understand and follow them.
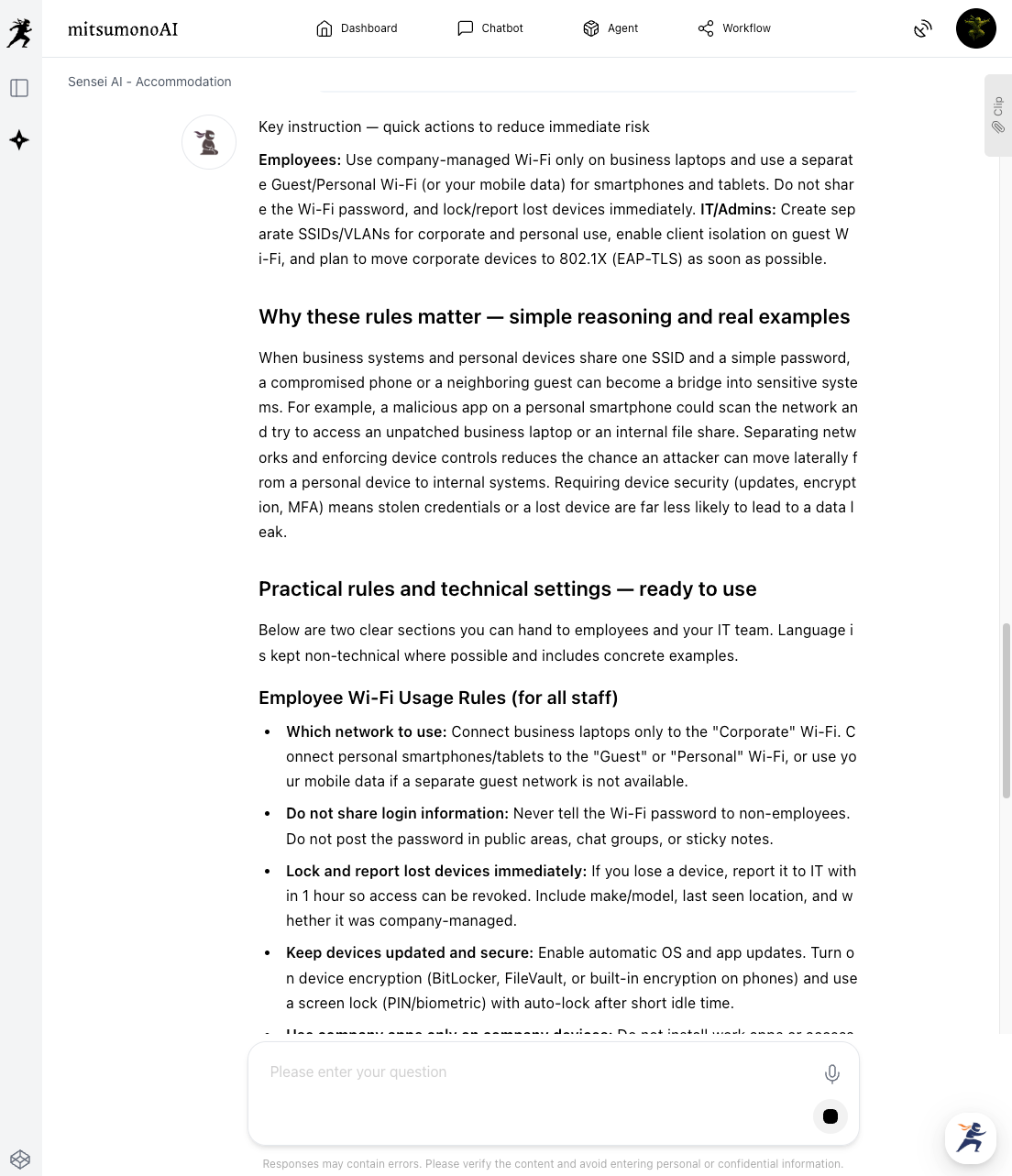
Review the rules and recommendations generated by the AI and adjust them to fit your company's specific environment.
Step 3: Ensuring Adoption and Maintaining Continuous Security
After reviewing and adjusting the AI-generated rules and recommendations, begin official implementation. When introducing the rules, explain why they are necessary. Use manuals and hold regular briefings or training sessions to ensure all employees fully understand them.
Example Roles for the IT Department/Staff
Based on the AI's recommendations, the IT department will plan and execute specific settings:
- Network Segmentation: Separate SSIDs for business system access and general internet use (consider implementing VLANs*).
- Strengthening Authentication: Use complex passwords of at least 12 characters and consider Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- Access Control: Implement MAC address filtering or restrict usage by time and location.
- Regular Monitoring: Build a system for monitoring network logs and detecting anomalies.
*VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network): A technology that logically divides a single physical network into multiple isolated networks.
Example Roles for All Employees
Employees must use Wi-Fi appropriately based on the established rules:
- Compliance with established rules (connecting to the correct network, proper password management, etc.).
- Implementing recommended security settings (OS updates, installing security software, etc.).
- Promptly reporting any suspicious activity or anomalies.
By reviewing rules and settings at least once a year—considering technological advances, new threats, and employee feedback—you can maintain a robust security framework through a continuous PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle.
Expected Results
Reduced Risk of Data Leaks and Improved Security Clear rules and proper security settings significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Increased Employee Security Awareness Through specific rules and education, individual security awareness grows, raising the overall security level of the organization. Improved IT Efficiency and Reduced Workload Using AI streamlines the initial stages of rule development and recommendation gathering, allowing IT staff to focus on critical operations and improvements.
Target Metrics (3 Months After Implementation)
KGI (Key Goal Indicator):
- Number of data leaks or security incidents related to employee Wi-Fi: 0
KPI (Key Performance Indicators):
- Employee awareness of Wi-Fi rules (via briefings, manuals, and tests): 90%+
- Compliance rate with security recommendations (e.g., complex passwords, OS updates): 85%+
- Frequency of employee security education: At least once a month




